Venezuela's Methane Problem Looms Over Trump's Oil Revival Plan
President Trump’s push to revive Venezuela’s oil sector is colliding with a major technical obstacle: vast methane leaks from crumbling infrastructure that could scare off large international investors, according to Bloomberg.
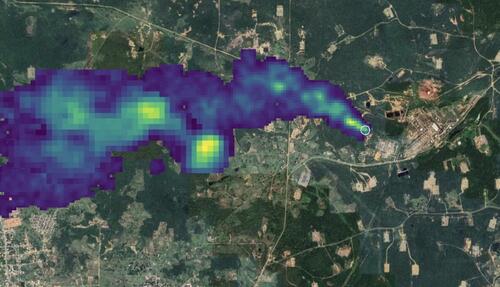
Satellite monitoring shows huge plumes of methane rising from abandoned rigs, corroded pipelines and aging facilities across the country. Those emissions signal both lost revenue and deep operational problems — conditions that tend to deter major oil companies. As Clayton Nash of Tegre Corp. put it, “That’s one way that you’re going to know that you’ve got facilities that are not operated well.”
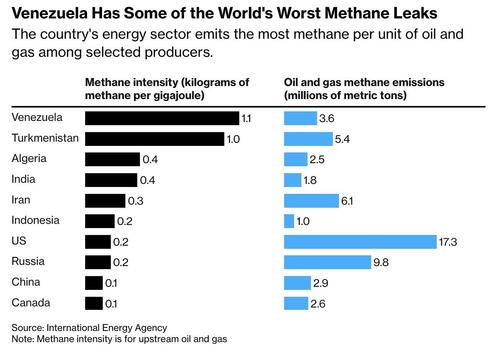
Each year Venezuela wastes about 13 billion cubic meters of natural gas through flaring, venting and leaks, roughly $1.4 billion in potential revenue. About a quarter of its total gas output escapes into the atmosphere — the highest rate globally and nearly ten times the world average. The scale of those leaks reflects decades of neglect, theft and underinvestment, leaving what remains of the system fragile and costly to repair.
Bloomberg writes that those realities complicate Trump’s effort to draw fresh capital. The White House is bringing U.S. oil executives to Washington on Friday to advance that plan, with the core message expected to be: “Do it for our country.” Yet analysts warn that political instability and Venezuela’s history of seizing foreign assets may keep major companies on the sidelines.
“We anticipate that large, publicly traded US and European majors will remain hesitant given their checkered history in the region,” said Quentin Peyle of Kayrros SA. “Instead, investment will likely come from smaller operators with a higher risk appetite.”
That shift carries its own risks. Smaller firms often lack the capital and incentives needed to modernize operations and control emissions at scale. Even if leaks are reduced, Deborah Gordon of RMI cautioned that “Venezuela’s fields will not only need an overhaul but also require careful operational management and oversight long into the future,” adding that the country’s extra-heavy crude would remain a major source of CO₂.
Restoring production near Venezuela’s former peak of almost 4 million barrels per day could require about $100 billion over the next decade. And the true condition of the infrastructure may remain hidden until output increases. As Nash warned, “You’re not going to find out how bad things are until you ramp up production.”